The Importance of Regular Hearing Check-ups with Professionals
You’re probably aware of the need for bi-annual dentist
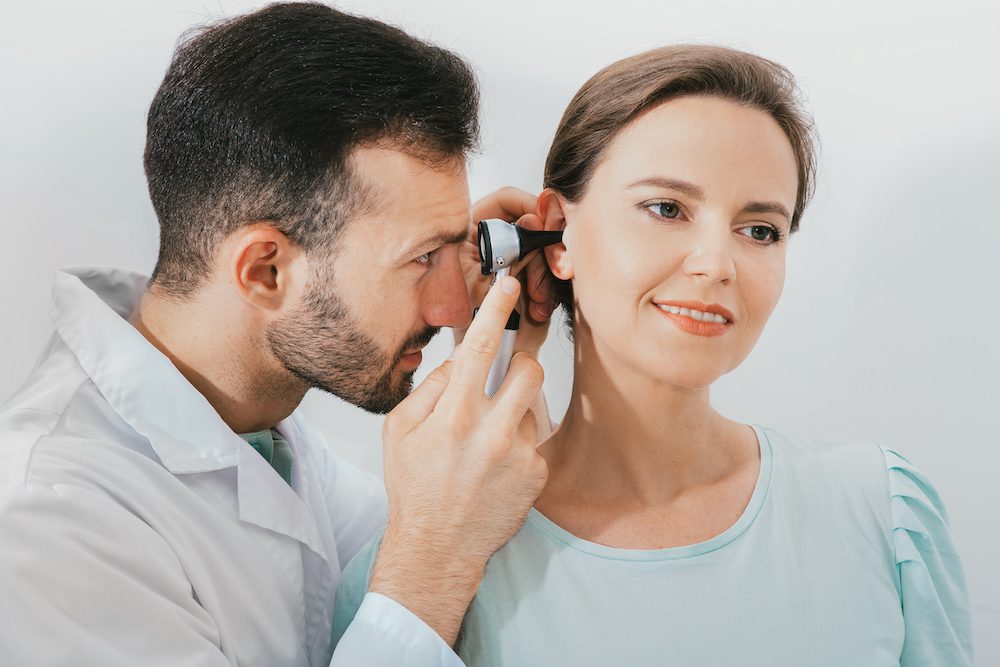

We should all be proactive about our health, and most of us know that regular visits to the doctors, dentists and opticians is always a good thing to detect any issues early on. But when it comes to our hearing health, this is often overlooked. It’s recommended that most people have a hearing test every three to five years, if you have any cause for concern or work a particularly noisy job then it might be more frequent.
Hearing tests are simple and painless, so if they’re not something you’ve ever thought to have done then here’s what you need to know.
Your hearing test won’t take place in your general practitioner’s office. If you have contacted your doctor because you suspect you’re experiencing hearing issues, then they will refer you to a hearing health professional that can conduct the testing you need to determine the extent of your hearing loss.
A hearing test takes around twenty to thirty minutes. You should be prepared to talk about all of the issues you have with your hearing, and to get the most out of your appointment it’s worth having any questions written down ahead of time so you don’t forget to ask. It’s often worth bringing someone with you to the test who may be able to help you answer some of the questions – some people might not realize their hearing is as affected as it is. Another person helping you answer might give the hearing care provider a more complete picture of your hearing health.
Hearing tests are carried out in a quiet environment which is insulated from external noise. You sit and listen to sounds transmitted by the hearing professional and press a button to signal when you have heard something. Tests include pure-tone audiometry, which includes listening to tones at different pitches and volumes. Speech audiometry is another component of most hearing tests and it uses recorded or live speech.
A tympanometry test will determine how well your eardrum is moving and will measure the reflexive responses of the middle ear muscles. Your results are plotted on a chart and afterwards are interpreted by the hearing care provider who will advise you if any action is needed.
Hearing loss is measured in decibels (dBs) and in the following categories:
It’s important to take care of all areas of your health, so don’t let your hearing health be overlooked. Even if you feel as though you can hear well now, a hearing test can let you know if any early signs are present and if so, what you can do about them.

You’re probably aware of the need for bi-annual dentist
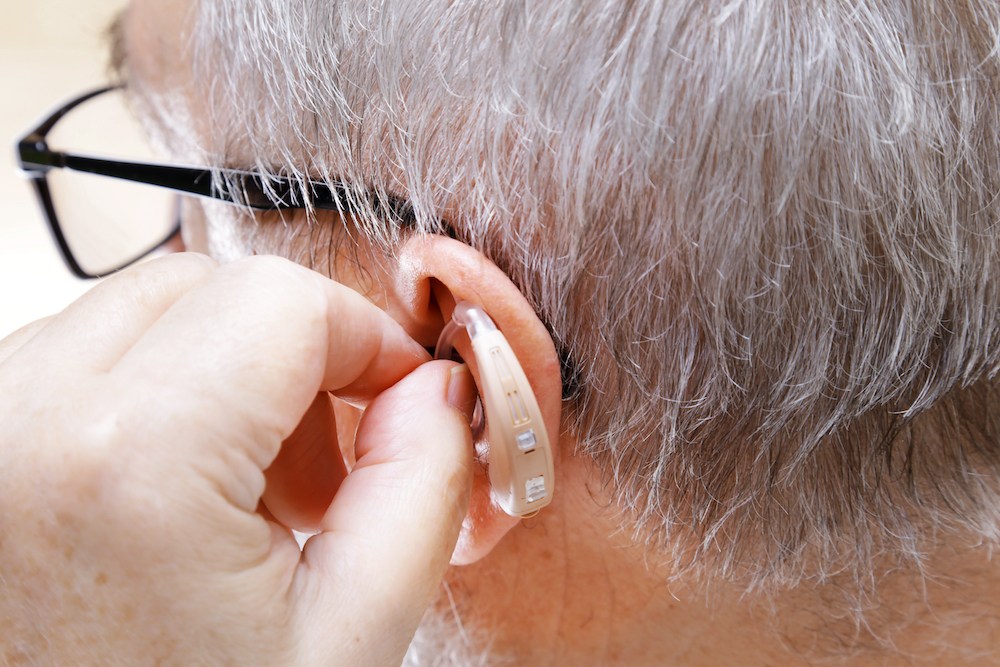
Choosing the right hearing aids is an important decision that can affect

A sudden loss of hearing is often noticeable right away, whether it’s